Introduction to Supply Chain
Supply chains are the backbone of modern commerce, connecting manufacturers, suppliers, distributors, retailers, and consumers in a complex network. The efficiency and transparency of supply chains play a vital role in meeting customer demands, reducing costs, and ensuring the delivery of high-quality products. However, traditional supply chain management often faces challenges such as data silos, lack of transparency, counterfeiting, and inefficiencies. Blockchain technology emerges as a game-changer in revolutionizing supply chains and optimizing their performance. In this article, we explore the concept of supply chains, the challenges they face, and how blockchain technology is transforming supply chain management to achieve unprecedented efficiency and reliability.
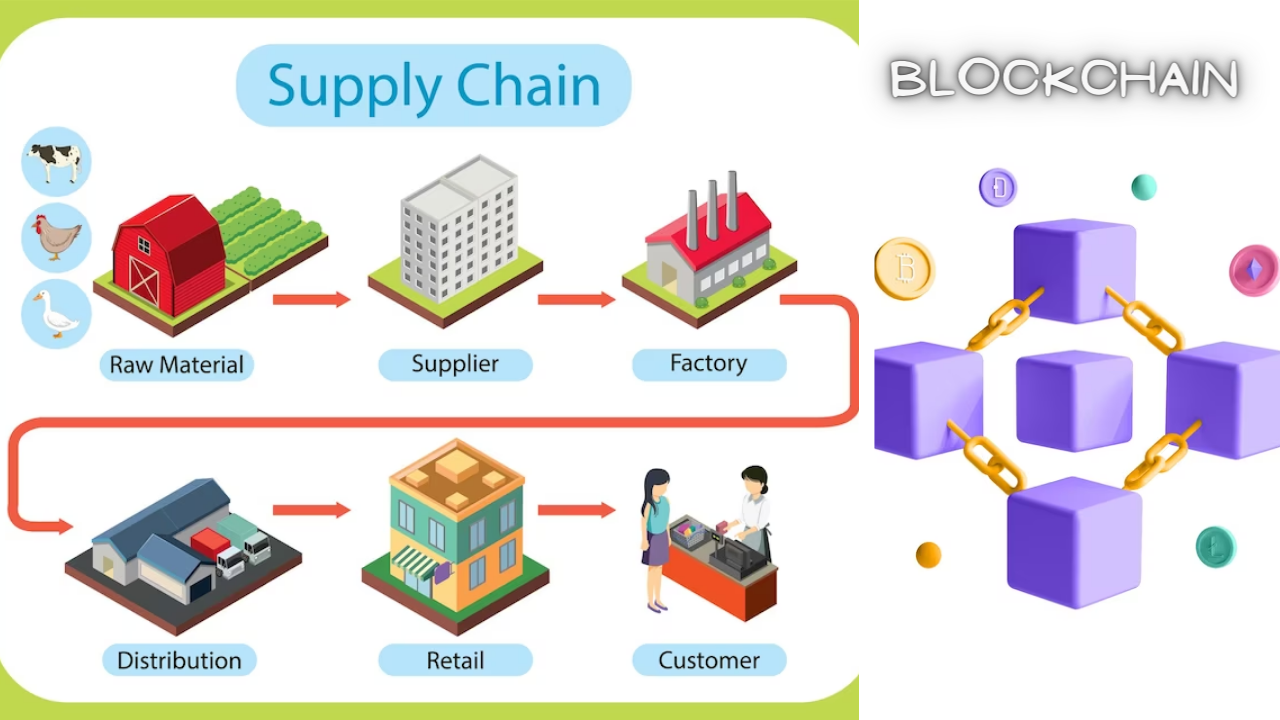
Understanding Supply Chains
A supply chain is a series of interconnected activities and processes that enable the flow of goods and services from raw material acquisition to the end consumer. It involves a complex network of suppliers, manufacturers, logistics providers, and retailers, each contributing to the production and distribution of goods. The efficiency of a supply chain is crucial in meeting market demands, maintaining product quality, and ensuring timely deliveries.
Challenges in Traditional Supply Chain Management
Traditional supply chain management faces several challenges that hinder its efficiency and transparency:
- Lack of Transparency: Traditional supply chains often suffer from information gaps, making it difficult to track the movement of goods and verify product authenticity.
- Inefficient Data Sharing: Data silos among supply chain participants lead to fragmented information, making decision-making cumbersome and slow.
- Counterfeiting and Fraud: Counterfeit products are a persistent issue in supply chains, leading to revenue loss and reputational damage for businesses.
- Inaccurate Inventory Management: Inadequate visibility into inventory levels can result in stockouts or overstocking, leading to increased costs and dissatisfied customers.
- Manual Processes: Many supply chain operations involve time-consuming manual processes, making them susceptible to errors and inefficiencies.
What is Blockchain?
Blockchain is a decentralized and distributed digital ledger technology that allows data to be recorded and shared across multiple participants in a secure, transparent, and tamper-resistant manner. It was originally introduced as the underlying technology for the digital currency Bitcoin, but its potential applications extend far beyond cryptocurrencies.
At its core, a blockchain consists of a chain of blocks, each containing a list of transactions or data records. Each block is linked to the previous one through cryptographic hashes, creating a chain of blocks with a chronological order. Once a block is added to the chain, it cannot be altered or deleted, ensuring the integrity of the data.
Key characteristics of blockchain technology include:
- Decentralization: Blockchain operates on a peer-to-peer network, where every participant (node) has access to the entire ledger. There is no central authority, making it a decentralized system.
- Security: The data in each block is secured through cryptographic hashing, which ensures that any change to the data will be immediately detected. Moreover, consensus mechanisms, such as Proof of Work (PoW) or Proof of Stake (PoS), validate and secure the transactions.
- Transparency: All participants in the network can view and access the same data, enhancing transparency and trust among users.
- Immutability: Once data is recorded in a block, it becomes immutable and cannot be altered or deleted. Any changes require consensus from the majority of the network.
- Consensus Mechanisms: To validate transactions and reach agreement on the state of the ledger, blockchain networks use consensus mechanisms. These mechanisms ensure that the majority of participants agree on the validity of transactions.
Blockchain in Supply Chain Optimization
Blockchain technology offers a decentralized, transparent, and secure platform that addresses these challenges, leading to a paradigm shift in supply chain optimization:
- Enhanced Traceability and Transparency: Blockchain’s immutable ledger records each transaction in the supply chain, creating an unalterable trail of product movements. This transparency enables real-time traceability, allowing businesses to identify inefficiencies and optimize supply chain processes.
- Real-time Data Sharing: Blockchain enables seamless data sharing among supply chain participants, fostering collaboration, and enabling quicker responses to changing demands and disruptions.
- Smart Contracts for Automation: Smart contracts execute predefined actions automatically when specific conditions are met. These contracts can automate tasks such as payments, order fulfillment, and compliance, streamlining the supply chain.
- Anti-Counterfeiting Measures: With blockchain, every product can be assigned a unique digital identifier that verifies its authenticity. This helps in combating counterfeiting and ensuring consumers receive genuine products.
- Supply Chain Finance: Blockchain’s transparent and verified data facilitates supply chain finance, allowing financial institutions to offer cost-effective financing solutions based on actual supply chain activities.
- Efficient Inventory Management: Real-time visibility into inventory levels helps businesses optimize stock levels, reduce carrying costs, and avoid stockouts or overstocking.
- Improved Compliance and Sustainability: Blockchain ensures the verification of products’ origins and adherence to environmental and social standards, enhancing compliance and sustainability efforts.
- Reduction in Fraud and Errors: Blockchain’s decentralized nature eliminates the need for intermediaries, reducing the chances of fraud and errors in supply chain processes.
How to actually Implement Blockchain Technology in SCM?
Implementing blockchain technology in supply chain management (SCM) requires careful planning, collaboration with stakeholders, and consideration of the specific requirements of the supply chain. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you implement blockchain in SCM effectively:
- Identify Use Cases: Start by identifying the specific use cases where blockchain can add value to your supply chain. Common use cases include traceability of products, anti-counterfeiting measures, supplier verification, inventory management, and smart contracts for automated transactions. Prioritize the most critical use case(s) that align with your supply chain’s pain points and goals.
- Choose the Right Blockchain Platform: Select the appropriate blockchain platform based on your requirements, such as public, private, or consortium blockchains. Evaluate factors like scalability, security, consensus mechanisms, and ease of integration with existing systems.
- Build a Consortium: In many supply chains, multiple stakeholders are involved, including suppliers, manufacturers, logistics providers, and retailers. Building a consortium of trusted partners is essential to ensure effective data sharing and collaboration. All members should agree to participate and adhere to the rules defined for data sharing and governance.
- Data Standardization and Integration: Establish data standards to ensure uniformity and compatibility of data across the supply chain. Integrate your existing systems with the blockchain network to enable seamless data exchange and real-time updates.
- Design Smart Contracts: For automated and self-executing processes, design smart contracts that define the conditions and actions to be executed when specific events occur. Ensure that all parties involved understand and agree to the terms defined in the smart contracts.
- Develop the Blockchain Network: Create the blockchain network, configure nodes, and set up consensus mechanisms. Define the access controls and permissions to ensure that only authorized participants can access and validate transactions.
- Onboarding and Training: Educate all participants about the benefits and functionalities of the blockchain network. Provide training on how to use the platform effectively and comply with the established protocols.
- Pilot Test: Conduct a pilot test of the blockchain implementation with a small segment of your supply chain. Evaluate the results and gather feedback from participants to identify any areas for improvement.
- Scale Up: After successful pilot testing, scale up the implementation across the entire supply chain. Monitor the performance of the blockchain network and address any issues that arise.
- Security and Privacy: Prioritize security and privacy measures to protect sensitive data. Implement robust encryption, authentication, and access controls to safeguard data from unauthorized access.
- Continuous Improvement: Continuously monitor the blockchain implementation, gather feedback from stakeholders, and make necessary adjustments to optimize its performance and address any evolving needs.
Conclusion
Blockchain technology is revolutionizing supply chains by introducing transparency, traceability, and automation, thereby optimizing efficiency and reliability. Through its decentralized and secure nature, blockchain addresses the challenges faced by traditional supply chain management, leading to significant cost savings, enhanced customer satisfaction, and sustainable business practices. As businesses increasingly recognize the potential of blockchain in supply chain optimization, its widespread adoption promises a future of seamless, efficient, and transparent supply chains, revolutionizing the world of commerce.
